It’s that time of year again, when many of us sit down to complete our income tax return and hope that we have done enough preparation to ensure a smooth and speedy process. Unfortunately, there are a number of complexities that can cause us problems – here are a few of the most common issues experienced by individuals when submitting their tax returns:
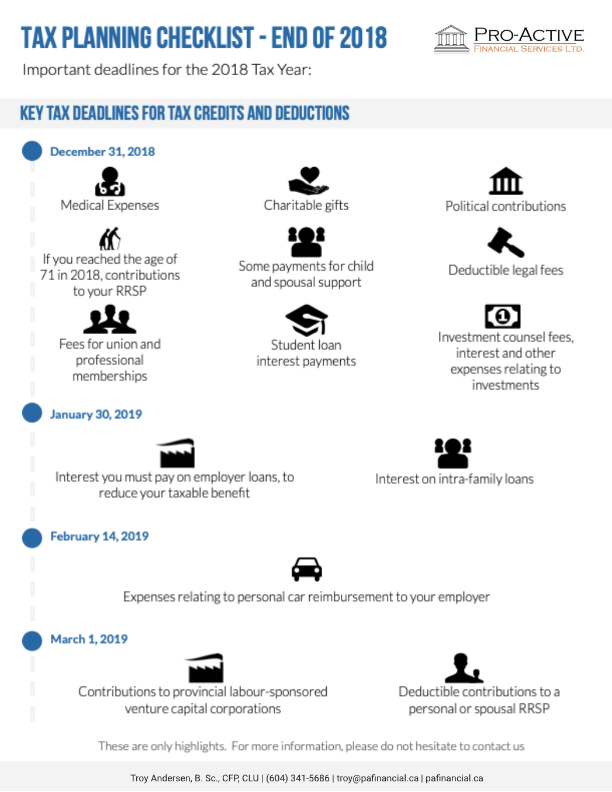
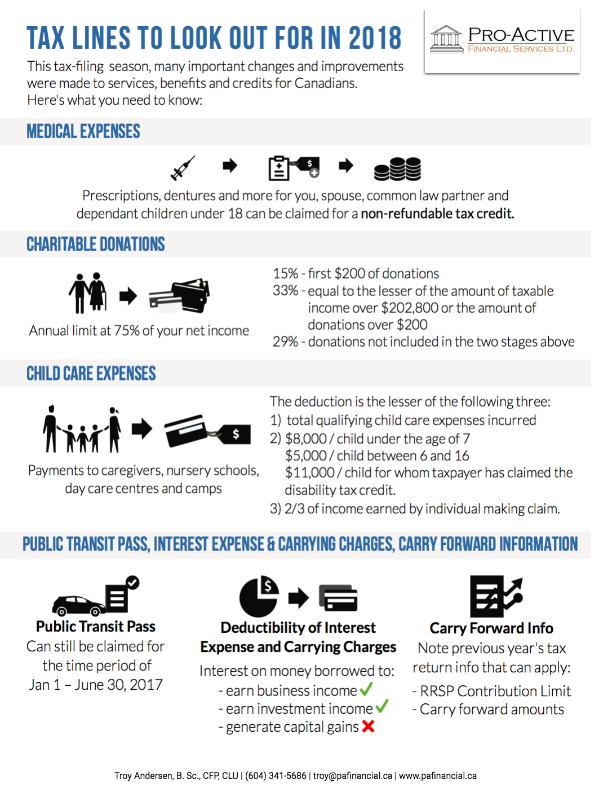
Medical Expenses
Expenses relating to medical expenses such as prescriptions, dentures and many more can be claimed for a non-refundable tax credit. You should also be aware that you can claim for yourself, your spouse or common law partner and any dependent children under the age of 18. You can also claim for certain other individuals whom you can clearly evidence are dependent on you (and the list of such individuals has recently been widened and can include grandparents, uncles, aunts, nieces and nephews).
Charitable Donations
You can claim tax credits for qualifying charitable donations that you made in 2017, though they are subject to an annual limit at 75% of your net income. You may also be eligible for a provisional donation tax credit. To receive such credits, you must supply a charitable donation receipt as evidence of your donation.
What’s more, there is a new formula for calculating the federal tax credit, depending on the value of donations. This is as follows:
1. 15% of the first $200 of donations
2. 33% of donations equal to the lesser of the amount of taxable income over $202,800 or the amount of donations over $200
3. 29% of total donations not included in the two stages above.
Public Transit Pass
Although this credit ended in the 2017 federal budget, it can still be claimed for the time period of January 1 – June 30, 2017. There are a range of eligible passes, including passes allowing unlimited travel within Canada, short term passes allowing unlimited travel for five days of which at least 20 days’ worth are purchased during a 28 day period and electronic payment cards.
Interest Expense and carrying charges
Interest on money borrowed to earn business or investment income is generally deductible, however interest expenses incurred on money borrowed to generate a capital gain is not tax deductible.
Carry forward information
Take note of the notice of assessment from your previous year’s tax return as it will contain important information that will apply to the submission of your current year’s return, such as your RRSP contribution limit and any carry-forward amounts.
Remember that you may be required to submit receipts alongside your electronic return at a later date, as requested by the CRA.
Child care expenses
Child care expenses include payments made to caregivers, nursery schools, day care centres and camps and other similar institutions. The deduction is usually best claimed by the lower earning spouse.
The deduction is the lesser of the following three:
· the total qualifying child care expenses which have been incurred
· $8,000 for each child under the age of 7, as well as $5,000 for each child between 6 and 16 and $11,000 for each child for whom the taxpayer has claimed the disability tax credit.
· two thirds of the income earned by the individual making the claim.
If you owe money when your income tax return is complete, the only way to delay payment is to delay the filing until the April 30th deadline. Alternatively, if CRA owes you money, then file as early as possible.