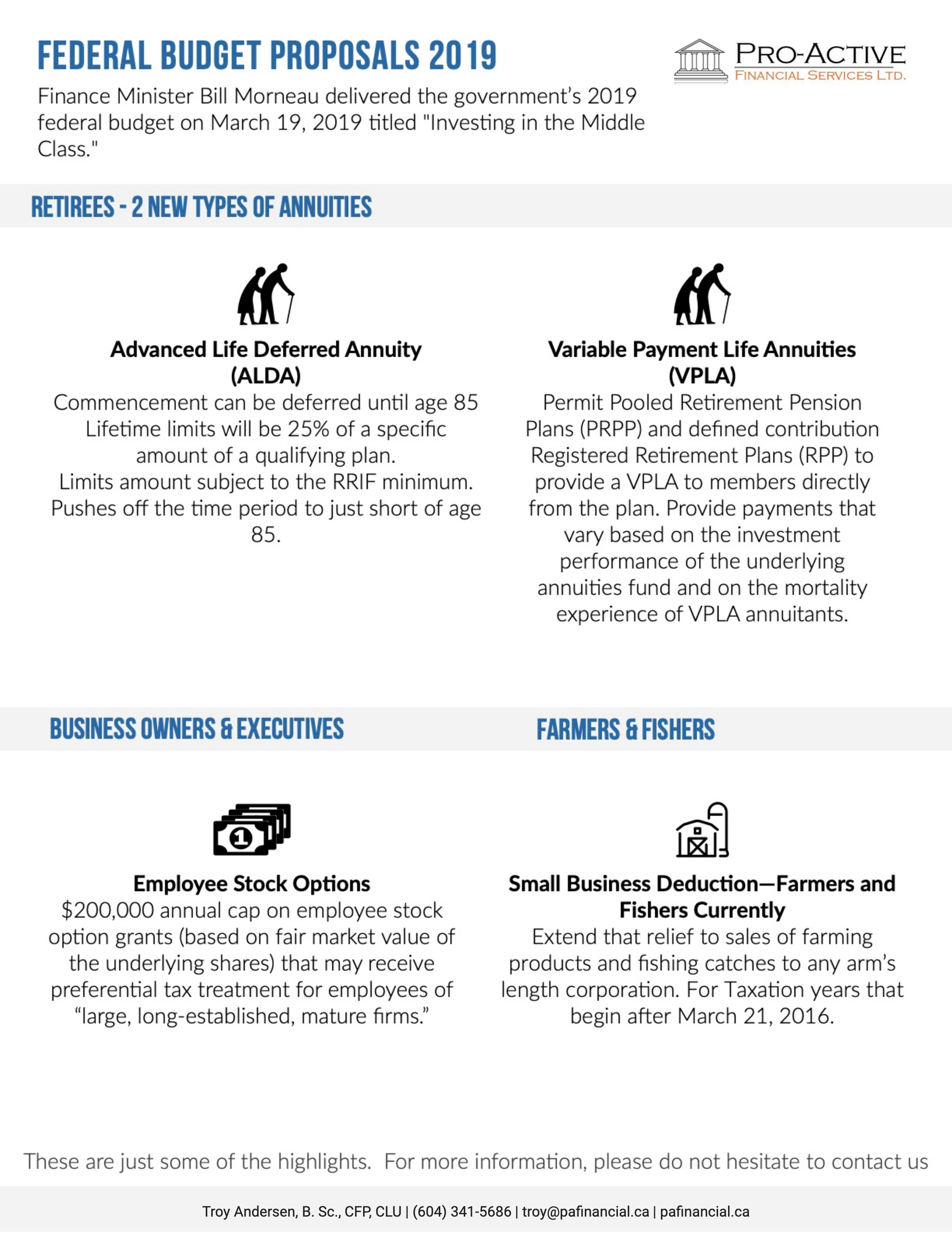
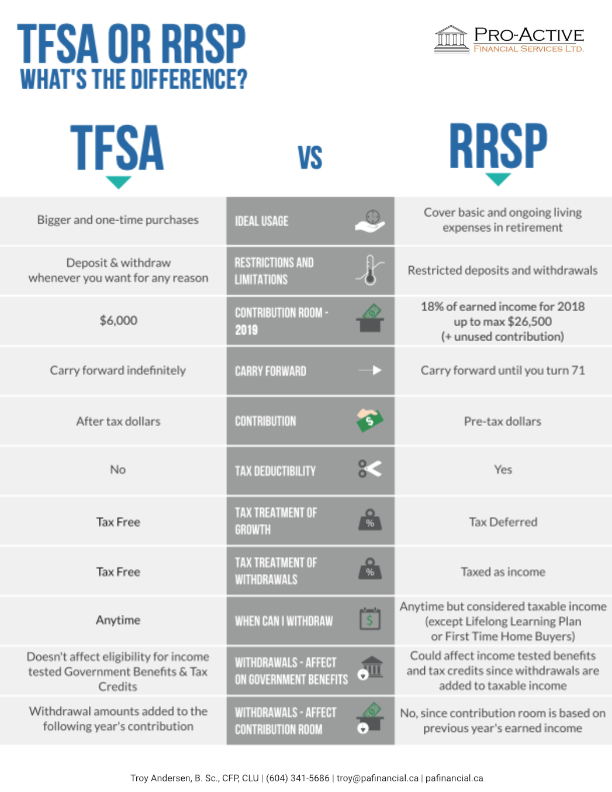
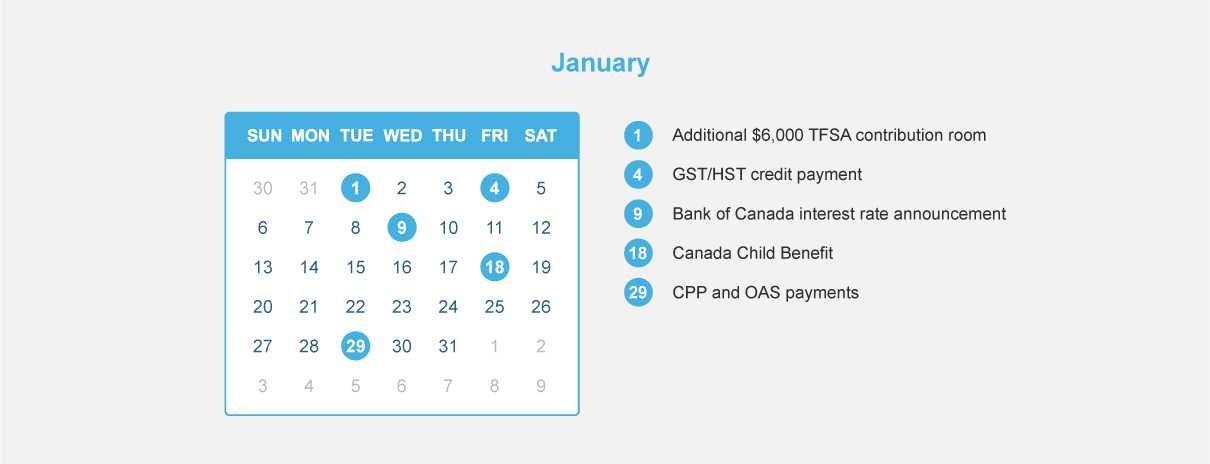
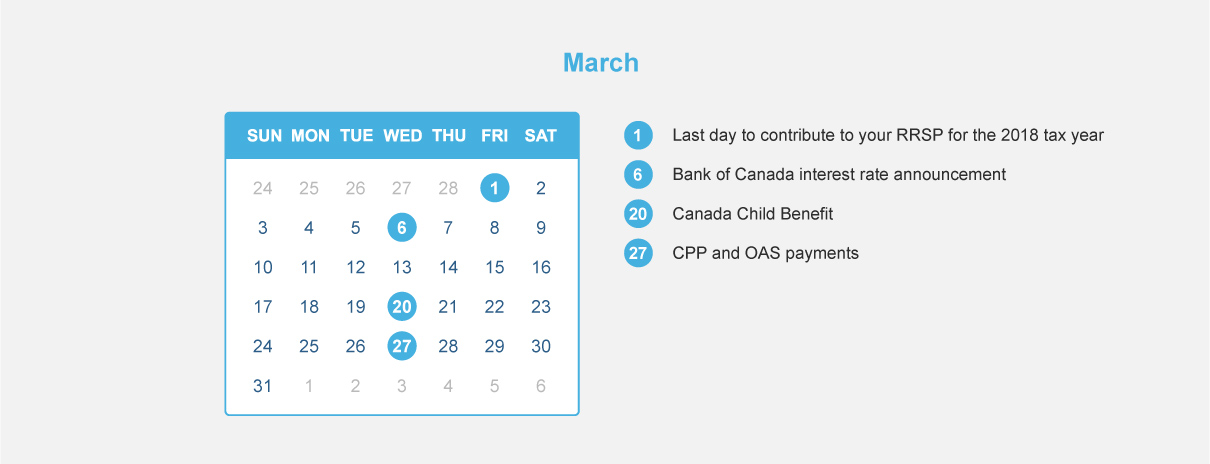
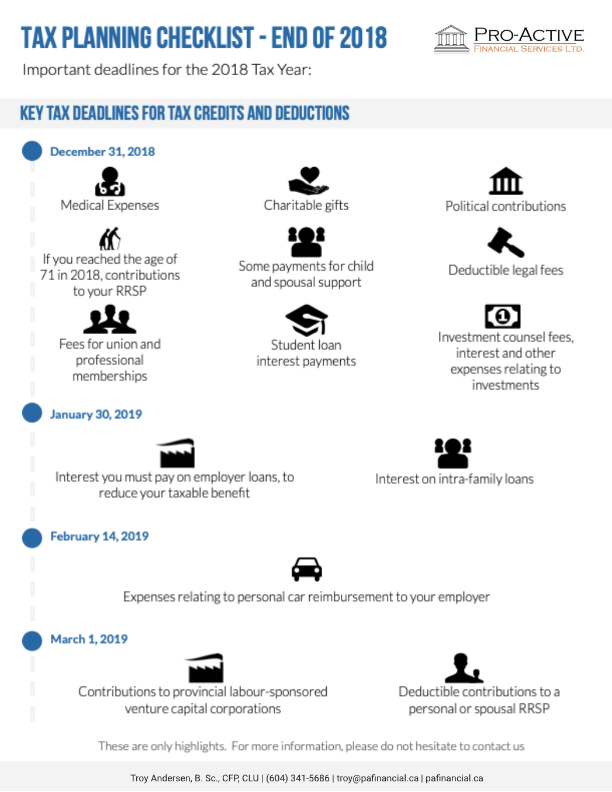
Real Estate or Investments?
One of the age-old financial quandaries asked of financial advisors is “shall I invest in property or funds?”. Predictably, the answer is not at all straightforward and depends on many factors, including your own financial style, personality and circumstances. Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of each choice to help you to be better informed about which could be the most lucrative option for you:
Benefits of investing in funds
It’s all too easy to go along with the generally-accepted myth that investing in property is a sure-fire way to secure your financial future. After all, house prices have appreciated in general terms for several years now and have become a very popular way for young people to invest for the future – this could also be, in part, down to the fact that their parents have benefited from the property booms of the past and made their own money this way, therefore presume the same will work for their children.
It’s fair to say, then, that investing the stock market is a much less common and popular way for people to invest their money. Despite market crashes, long term fund ownership is hands down the greatest creator of wealth in history and high quality funds generally not only increase their profits every year but also pay out increased cash dividends too.
Other advantages of fund ownership include the fact that you can diversify your portfolio easily, borrow against your funds easily and also benefit from the fact that funds are much more liquid than real estate, giving you maximum financial flexibility.
So, why do fewer people invest in funds than real estate?
It could be due to the two market crashes that have occurred since 2000, making people wary of getting involved in what they perhaps see as a complex and inherently risky way to make money. Many fail to take the long-term view of funds and the fact that, to financially benefit in the best way, you need to ride the highs and lows for a number of years to get a good return on your initial investment.
Another reason could be the fact that many people underestimate the real cost of home ownership. Additional costs such as maintenance, insurance and mortgage interest must be factored into investment calculations but are often not, making property a seemingly more attractive investment option.
Drawbacks of investing in funds
You really have to be in this game for the long term to see your money grow consistently and many people don’t have the discipline or patience to hold their nerve and keep their money in the same place for a prolonged period. This can often result in cashing in one’s funds too early and missing out on long term benefits. Similarly, because the prices of funds can fluctuate so much, many are too nervous about investing and don’t see the opportunities to purchase more funds at reduced prices to benefit them in the long term.
Benefits of investing in real estate
Many individuals in their twenties and thirties who are just starting out thinking about how best to secure their financial future feel more comfortable with investing in property and the notion of “owning one’s own home” – likely brought about by their parents’ influence, as discussed above. They perhaps feel more confident in the process, terminology and philosophy of real estate and believe that they are more likely to succeed in this area.
Another benefit could be the fact that, by purchasing a property, you feel that you own something tangible, as opposed to the money invested in funds and shares which could be said to exist only online or on paper.
Finally, many take comfort from the fact that it is potentially harder to be defrauded in relation to real estate as there are so many varied, physical checks that one can perform to verify the facts, such as property inspections, tenant background checks etc, whereas with funds, a lot of trust has to be given to the management company or auditors.
Drawbacks of investing in real estate
There are a number of hidden costs to real estate, particularly if your property is unoccupied for a period of time and you are still liable to pay taxes, maintenance etc. It’s also true that the maintenance of a property can be a time consuming as well as an expensive business, due to the requirement to deal with routine as well as emergency issues.
What’s more, it’s true that the actual value of real estate hardly ever increases in inflation-adjusted terms, therefore the returns can be healthy but the true value of the property doesn’t actually change. It’s due to this that many feel that investing in funds is a much more solid and lucrative way to receive good returns.
Talk to us, we can help you determine what works best for you.