2020 Financial Calendar
2020 Financial Calendar
Financial Calendar for 2020 – All the dates you need to know to maximize your benefits!
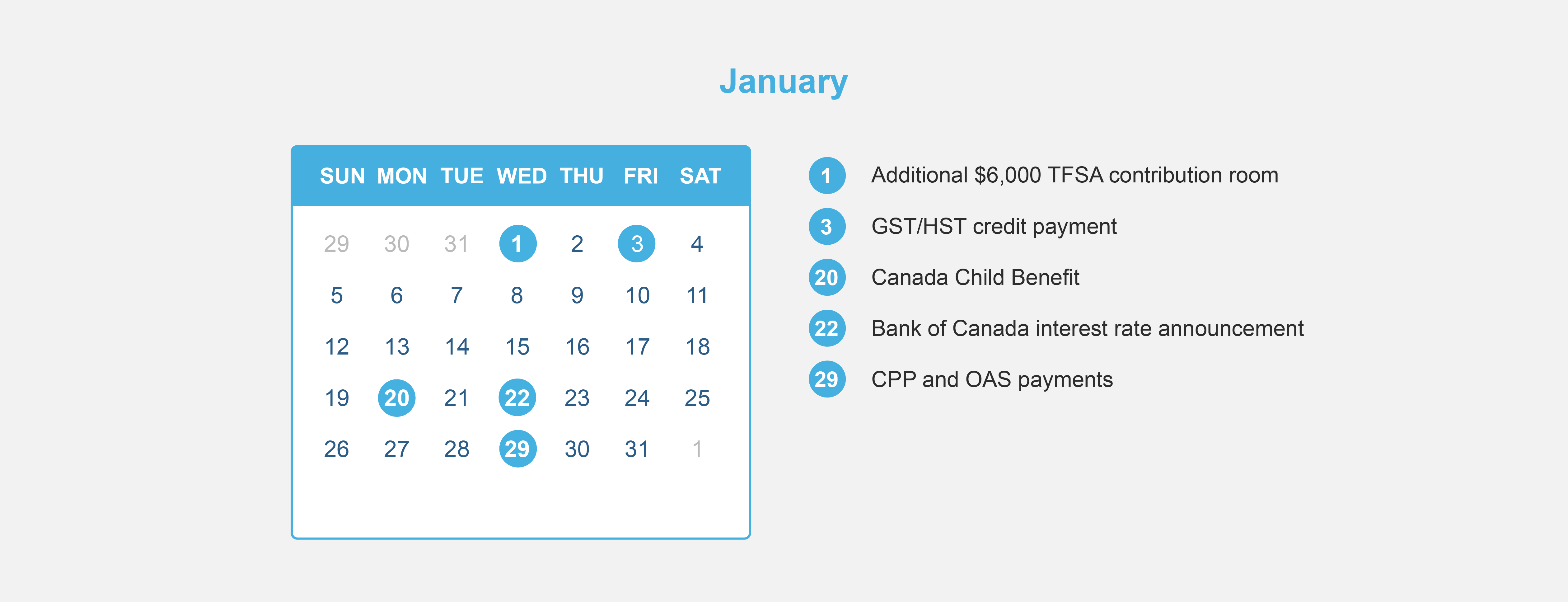










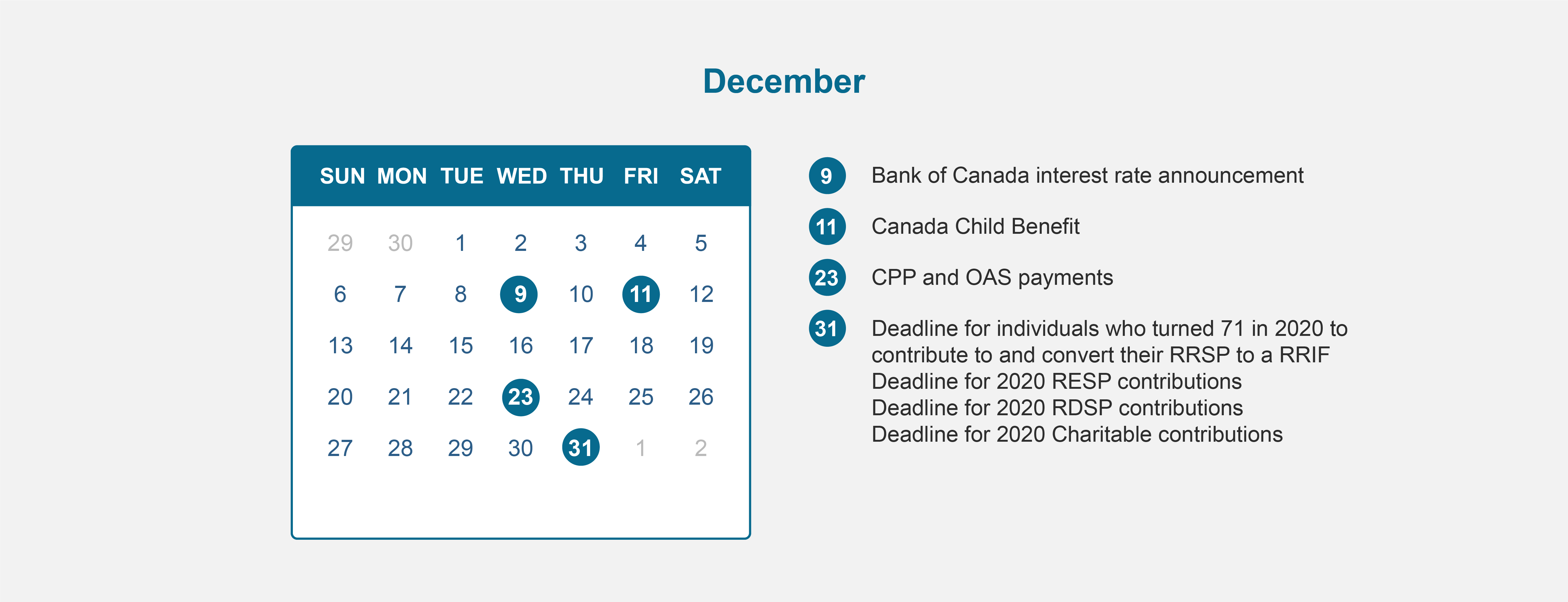
Financial Calendar for 2020 – All the dates you need to know to maximize your benefits!












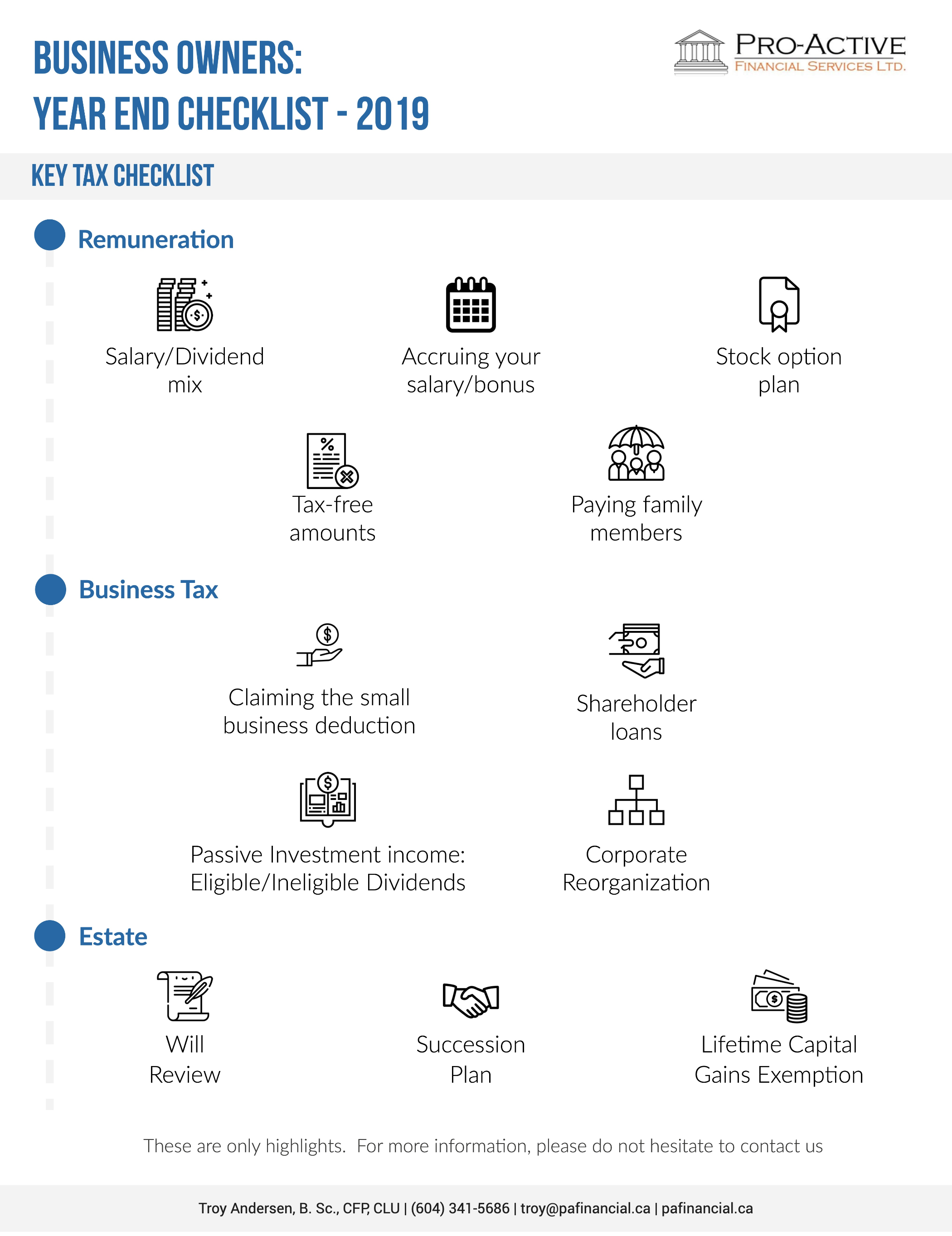
Now that we are nearing year end, it’s a great time to review your business finances. With the federal election over and no major business tax changes for this year, 2019 is a good year to make sure you are effectively tax planning. Please keep in mind that your business may be affected by the recent tax on split income (TOSI) and the passive investment income rules given they came into effect in 2018. These rules can be complicated, please don’t hesitate to consult us and your accountant to determine how this can affect your business finances.
We are also assuming that your corporate year end is December 31, however if it’s not, this is useful when your business year end comes up.
Below, we have listed some of the key areas to consider and provided you with some useful guidelines to make sure that you cover all of the essentials. We have divided our tax planning tips into 4 sections:
Tax checklist
Remuneration
Business tax
Estate
Remuneration
☐ Salary/Dividend mix
☐ Accruing your salary/bonus
☐ Stock option plan
☐ Tax-free amounts
☐ Paying family members
Business Tax
☐ Claiming the small business deduction
☐ Shareholder loans
☐ Passive investment income: eligible/ineligible dividends
☐ Corporate reorganization
Estate
☐ Will review
☐ Succession plan
☐ Lifetime capital gains exemption
What’s your salary/dividend mix?
Individuals who own incorporated businesses can elect to receive their income as either salary or as dividends. Your choice will depend on your own situation consider the following factors:
Your current and future cash flow needs
Your personal income level
The corporation’s income level
TOSI rules
Passive investment income rules
Please also consider the difference between salary and dividends:
Salary
✓ Provides RRSP contribution
✓ Reduces corporate tax bill
• Payroll tax
• Canada Pension Plan (CPP) contribution
• Employment Insurance contribution
Dividend
• Doesn’t provide RRSP contribution
• Doesn’t reduce corporate tax bill
• No tax withholdings
• No Canada Pension Plan contribution
• No Employment Insurance contribution
✓ Receive up to $50,000 of ineligible dividends at a low tax rate depending on province
As part of this, it’s worth considering ensuring that you receive a salary high enough to take full advantage of the maximum RRSP annual contribution that you can make. For 2019, salaries of $151,278 will provide the maximum RRSP room of $27,230 for 2020.
Is it worth accruing your salary or bonus this year?
You could consider accruing your salary and / or bonus in the current year but delaying payment of it until the following year. If your company’s year-end is December 31, your corporation will benefit from a deduction for the year 2019 and the source deductions are not required to be remitted until actual salary or bonus payment in 2020.
Stock Option Plan
If your compensation includes stock options, please check if you will be affected by the new proposed stock option rules. This caps the amount of certain employee stock options eligible for the stock option deduction at $200,000 after December 31, 2019. The rules will not affect you if your stock options are granted by a Canadian controlled private corporation.
Tax Free Amounts
If you own your corporation, pay tax-free amounts if you can. Here are some ways to do so:
Pay yourself rent if the company occupies space in your home.
Pay yourself capital dividends if your company has a balance in its capital dividend account.
Return “paid-up capital” that you have invested in your company
Do you employ members of your family?
Employing and paying salary to family members who undertake work for your incorporated business is worth considering as you could receive a tax deduction against the salary that you pay them, providing that said salary is “reasonable” in relation to the work done. In 2019, the individual can earn up to $12,069 and pay no federal tax. This also provides the individual with RRSP contribution room, CPP and allow for child-care deductions. Bear in mind additional costs that are incurred when employing someone, such as payroll taxes and contributions to CPP.
Claiming the Small Business Deduction
Are you able to claim a small business deduction? The federal small business tax rate decreased from 9% in 2019 (from 10% in 2018) and not anticipated to increase in 2020. From a provincial level, there will be changes in the following provinces:
Small Business Tax Rate
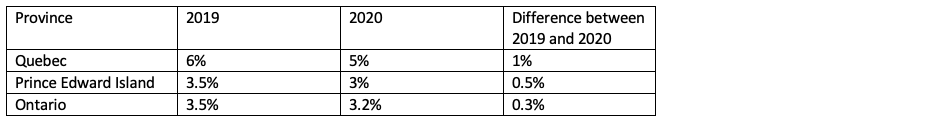
Therefore, a small business deduction in 2019 is worth more than in 2020 for these provinces.
Should you repay any shareholder loans?
Loaning funds from your corporation at a low or zero interest rate means that you are considered to have benefited from a taxable benefit at the CRA’s 2% interest rate, less actual interest that you pay during the year or thirty days after it. You need to include the loan in your income tax return, unless it is repaid within one year after the end of your corporation’s taxation year.
For example, if your company has a December 31st year-end and it loaned you funds on November 1, 2019, you must repay the loan by December 31, 2020, otherwise you will need to include the loan as taxable income in your 2019 personal tax return.
Passive investment income
If your corporation has a December year- end, then 2019 will be the first taxation year that the new passive investment income rules may apply to your company.
New measures were introduced in the 2018 federal budget relating to private businesses which also earn passive investment income in a corporation that also operates an active business.
There are two key parts to this, as follows:
Limiting access to dividend refunds. Essentially, a private company will be required to pay ineligible dividends in order to receive dividend refunds on some taxes which, in the past, could have been refunded when an eligible dividend was paid.
Limiting the small business deduction. This means that, for the companies mentioned above, the small business deduction can be reduced at a rate of $5 for every $1 over between $50,000 and $150,000 of investment income, or eliminated if investment income exceeds $150,000. Please note that Ontario and New Brunswick have indicated that they will not follow the federal rules.
If your corporation earns both active business and passive investment income, you should contact us and your accountant directly to determine if there are any planning opportunities to minimize the impact of the new passive investment income rules.
Think about when to pay dividends and dividend type
When choosing to pay dividends in 2019 or 2020, you should consider the following:
Difference between the yearly tax rate
Impact of tax on split income
Impact of passive investment income rules
With the exception of 2 provinces, Quebec and Ontario, the combined top marginal tax rates will not be changing from 2019 to 2020 on a provincial level. Therefore, it will not make a difference if you choose to pay in 2019 or 2020.
Combined Marginal Tax Rate
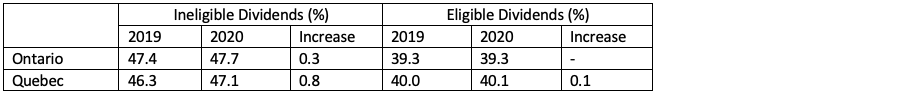
In Quebec and Ontario, because there are slight increases in the combined marginal tax rate, there are potential tax savings available if you choose to pay dividends in 2019 rather than in 2020.
When deciding to pay a dividend, you will need to decide to pay out eligible or ineligible dividends, you should consider the following:
Dividend refund claim limits: Eligible refundable dividend tax on hand (ERDTOH) vs Ineligible Refundable dividend tax on hand (NRDTOH)
Personal marginal tax rate of eligible vs. ineligible dividends
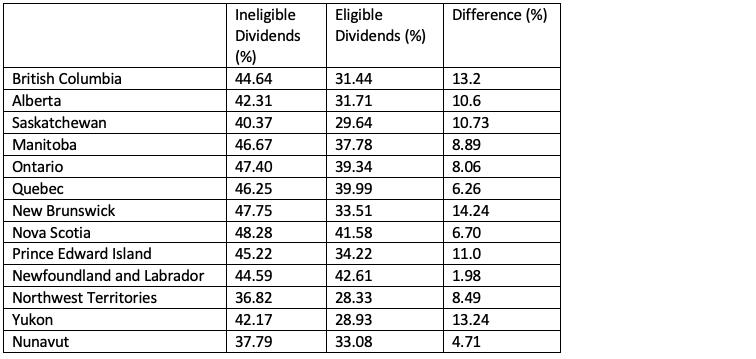
Given the passive investment income rules, typically, it makes sense to pay eligible dividends to deplete the ERDTOH balance before paying ineligible dividends. (Please note that ineligible dividends can also trigger a refund from the ERDTOH account.)
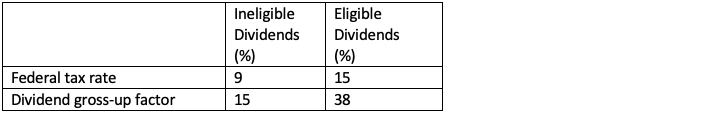
Eligible dividends are taxed at a lower personal tax rate than ineligible dividends (based on top combined marginal tax rate). However, keep in mind, when ineligible dividends are paid out, they are subject to the small business deduction, therefore the dividend gross-up is 15% while eligible dividends that are subject to the general corporate tax rate have a dividend gross-up is 38%. It’s important to talk to a professional to determine what makes the most sense when determining the type of dividend to pay out of your corporation.
Combined Personal Top Marginal Tax Rate on Dividends
Corporate Federal Tax Rate and Gross-up factor
Corporate Reorganization
It might be time to revisit your corporate structure given the changes to private corporation rules on income splitting and passive investment income to provide more control on the distribution of dividend income. Another reason to reassess your structure is to segregate investment assets from your operating company for asset protection. (Keep in mind you don’t want to trigger TOSI, so make sure you structure this properly.) If you are considering succession planning, this is the time to evaluate your corporate structure as well.
Ensure your will is up to date
In particular, if your estate plan includes an intention for your family members to inherit your business, ensure that this plan is tax effective following new tax legislation from January 1, 2016. In addition, review your will to make sure that any private company shares that you intend to leave won’t be affected by the new TOSI rules.
Succession plan
Consider a succession plan to ensure your business is transferred to your children, key employees or outside party in a tax efficient manner.
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption
If you sell your qualified small business corporation shares, you can qualify for the lifetime capital gains exemption (In 2019, the exemption is $866, 912) where the gain is completely exempt from tax. The exemption is a lifetime cumulative exemption; therefore, you don’t have to claim the entire amount at once.
The issues we discussed above can be complex. Contact us and your accountant if you have any questions, we can help.
Now that we are nearing year end, it’s a good time to review your finances. With the federal election over and no major tax personal tax changes for this year, 2019 is a good year to make sure you are effectively tax planning. Below, we have listed some of the key areas to consider and provided you with some useful guidelines to make sure that you cover all of the essentials. We have divided our tax planning tips into 4 sections:
Tax deadlines
Family tax issues
Managing your investments
Retirement planning
If you reached the age of 71 in 2019, contributions to your RRSP
Use up your TFSA contribution room
Contribute to RESP to get the Canadian education savings grant and the income-tested Canada learning bond.
Contribute to RDSP to get the Canada disability savings grant and the income-tested Canada disability savings bond.
Medical expenses
Investment counsel fees, interest and other expenses relating to investments
Some payments for child and spousal support
Fees for union and professional memberships
Student loan interest payments
Deductible legal fees
Charitable gifts
Political contributions
Interest on intra-family loans
Interest you must pay on employer loans, to reduce your taxable benefit
Contributions to provincial labour-sponsored venture capital corporations
Deductible contributions to a personal or spousal RRSP
RRSP Repayment under Home Buyers Plan or Lifelong Learning Plan

Check your eligibility to the Canada Child Benefit
In order to receive the Canada Child Benefit in 2020/21, you need to file your tax returns for 2019 because the benefit is calculated using the family income from the previous year. Eligibility depends on set criteria such as your family’s income and the number and age of your children and you may qualify for full or partial amount.
Consider family income splitting
The CRA offers a low interest rate on loans and it therefore makes sense to consider setting up an income splitting loan arrangements with members of your family, whereby you can potentially lock in the family loan at a low interest rate of 2% and subsequently invest the borrowed monies into a higher return investment and benefit from the lower tax status of your family member. Don’t forget to adhere to the Tax on Split Income rules.
Contribute to Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP)
The Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) is a savings plan for parents and others to save for a child’s education. The Canada education savings grant (CESG) will match up to 20% of contributions up to $2,500. That means the CESG can add a maximum of $500 to an RESP each year. Grant room accumulates until the child turns 17, therefore unused basic CESG amounts for the current year are carried forward for possible use in the future years. The income-tested Canada learning bond (CLB) is paid directly to the RESP by the Canadian government to low-income families. There are no personal contributions required to receive the CLB.
Contribute to Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP)
The Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) is a savings plan for parents and others to save for the financial security of a person who is eligible for the disability tax credit (DTC). The Canada disability savings grant will pay matching grants of 300%, 200% or 100% depending on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and amount contributed. The income-tested Canada disability savings bond is paid directly to the RDSP by the Canadian government to low- income Canadians with disabilities. Before December 31 of the year you turn 49 years old, you can carry forward up to 10 years of unused grant and bond entitlements to future years, as long as you met the eligibility requirements during the carry forward years.
Use up your TFSA contribution room
If you are able, it’s worth contributing the full $6,000 to your TFSA for 2019. You can also contribute more (up to $63,500) if you are 28 or older and haven’t made any previous TFSA contributions.
Contribute to Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP)
The Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) is a savings plan for parents and others to save for a child’s education. The Canada education savings grant (CESG) will match up to 20% of contributions up to $2,500. That means the CESG can add a maximum of $500 to an RESP each year. Grant room accumulates until the child turns 17, therefore unused basic CESG amounts for the current year are carried forward for possible use in the future years. The income-tested Canada learning bond (CLB) is paid directly to the RESP by the Canadian government to low-income families. There are no personal contributions required to receive the CLB.
Contribute to Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP)
The Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) is a savings plan for parents and others save for the financial security of a person who is eligible for the disability tax credit (DTC). The Canada disability savings grant will pay matching grants of 300%, 200% or 100% depending on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and amount contributed. The income-tested Canada disability savings bond is paid directly to the RDSP by the Canadian government to low- income Canadians with disabilities. Before December 31 of the year you turn 49 years old, you can carry forward up to 10 years of unused grant and bond entitlements to future years, as long as you met the eligibility requirements during the carry forward years.
Donate securities to charity
Make a donation by year end will provide you tax savings. If you donate eligible securities or mutual funds, capital gains tax does not apply, and you can receive a tax receipt for their full market value. Also, the charity gets the full value of the securities.
Think about selling any investments with unrealized capital losses
It might be worth doing this before year-end in order to apply the loss against any net capital gains achieved during the last three years. Any late trades should ideally be completed on or prior to December 24, 2019 and subsequently confirmed with your broker.
Conversely, if you have investments with unrealized capital gains which are not able to be offset with capital losses, it may be worth selling them after 2019 in order to be taxed on the income the following year.
Consider the timing of purchasing of certain non-registered investments
If you are considering purchasing an interest-bearing investment like a guaranteed investment certificate (GIC) with a maturity date of one year or more, you may consider delaying the purchase to the following year, so you don’t have to pay tax on accrued interest until 2021. You should also consider this with mutual funds that make taxable distributions before the end of 2019, consider delaying this until early 2020. Don’t pay taxes earlier than necessary.
Check if you have investments in a corporation
The new passive investment income rules apply to tax years from 2018. They state that the small business deduction is reduced for companies which are affected with between $50,000 and $150,000 of investment income, therefore the small business deduction has been stopped completely for corporations which earn passive investment income of more than $150,000. At a provincial level, Ontario and New Brunswick have indicated that they are not following the federal rules to limit access to the small business deduction.
Make the most of your RRSP
The deadline for making contributions to your RRSP for the year 2019 is February 29, 2020. There are three things that affect how much you may contribution towards your RRSP, as follows:
18% of your previous year’s earned income
Up to a maximum of $26,500 for 2019 and $27,230 for 2020
Your pension adjustment
Remember that deducting your RRSP contribution reduces your after-tax cost of making said contribution.
Check when your RRSP is due to end
You should wind-up your RRSP if you reached the age of 71 during 2019 and your final contributions should be made by December 31, 2019.
Convert to RRIF before year end
If you’re 65 or older in the year, you’re entitled to a pension credit that can fully or partly offset the tax on the first $2,000 of eligible income annually. Consider setting up a RRIF before year-end to pay out $2,000 annually if you don’t have any other eligible pension income.
Contact us if you have any questions, we can help.

Capital Dividend Account (CDA) is a special corporate tax account which gives shareholders designated capital dividends, tax-free. This account is not recorded in the corporation’s taxable accounting entries or financial statements. For this type of account, capital dividend is taken out from paid-in capital and not from retained earnings.
Business Owners
Shareholders of Private Business
Life insurance proceeds in excess of adjusted cost basis “(ACB)” “except” for increase in death benefit after 2013 when borrowing under a 10/8 arrangement.
Multi-life policies only have one ACB, therefore when each person under the policy dies, the ACB will reduce the credit to the CDA at each time of death.
When capital dividends are paid out to shareholders, these are not taxable. The Capital Dividend Account is part of a tax provision whose goal it is to enable tax-free money received by a company, to then be given to its shareholders, tax free. Therefore, shareholders are not required to pay taxes on these distributions.
The CDA can be complicated, please talk to us to see if this makes sense for your clients.

One of the financial planning issues that business owners face is how to access their corporate earnings in a tax efficient way.
There are 5 standard methods:
Salary
Dividend
Shareholder Loans
Transfer Personal Assets
Income Splitting
There are also unique ways utilizing life insurance and critical illness insurance to access your retained earnings. Please contact us to learn how we can get more money in your pocket than in the government’s.
An advisor can help you determine where you are today financially and where you want to go. An advisor can provide you guidance on how to reach your short, medium and long term financial goals.
Worry less about money and gain control.
Organize your finances.
Prioritize your goals.
Focus on the big picture.
Save money to reach your goals.
Advisors can help you with accumulation and protection
Accumulation:
Cash Management – Savings and Debt
Tax Planning
Investments
Protection:
Insurance Planning
Health Insurance
Estate Planning
Establish and define the financial advisor-client relationship.
Gather information about current financial situation and goals including lifestyle goals.
Analyze and evaluate current financial status.
Develop and present strategies and solutions to achieve goals.
Implement recommendations.
Monitor and review recommendations. Adjust if necessary.
Talk to us about helping you get your finances in order so you can achieve your lifestyle and financial goals.
Feel confident in knowing you have a plan to get to your goals.
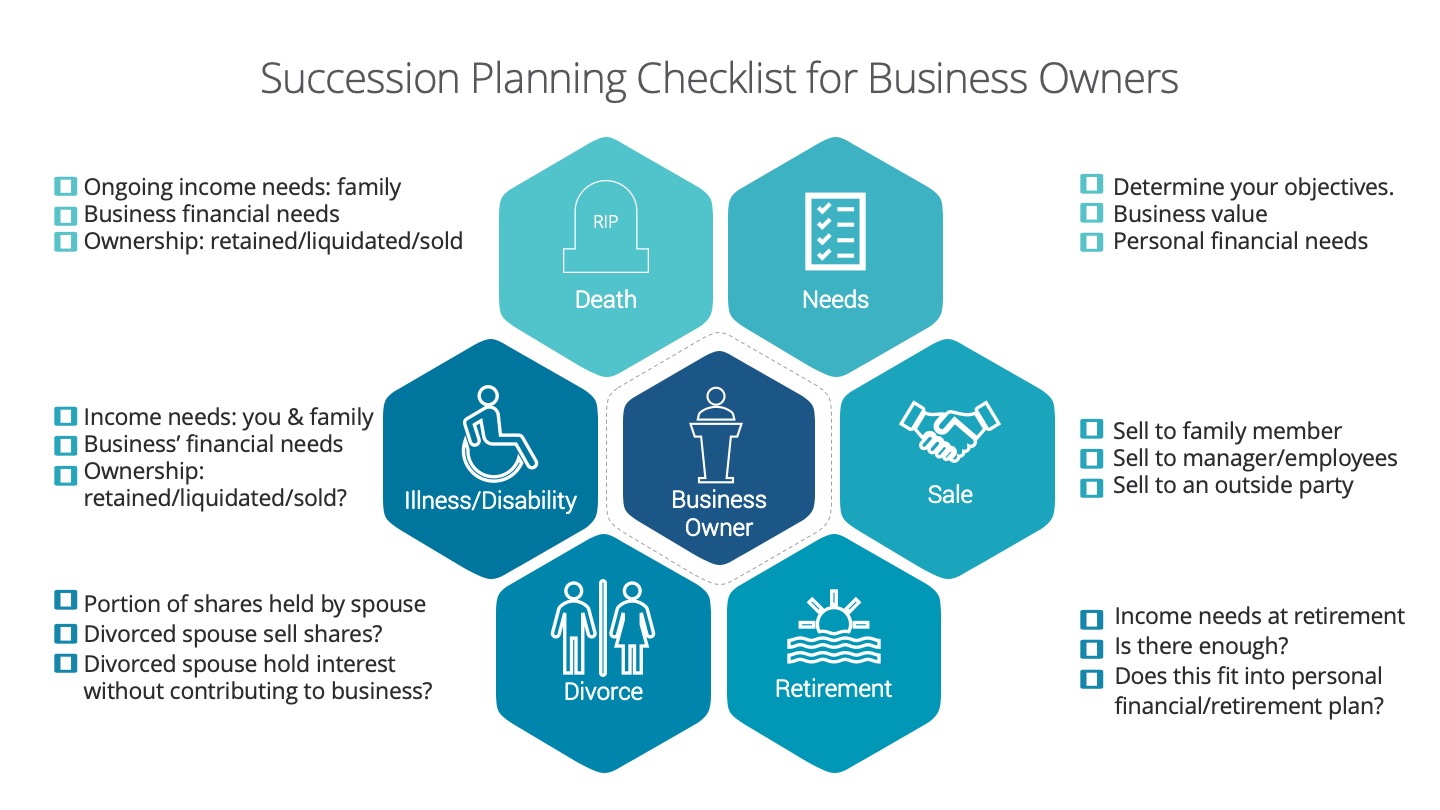
Business owners deal with a unique set of challenges. One of these challenges includes succession planning. A succession plan is the process of the transfer of ownership, management and interest of a business. When should a business owner have a succession plan? A succession plan is required through the survival, growth and maturity stage of a business. All business owners, partners and shareholders should have a plan in place during these business stages.
We created this infographic checklist to be used as a guideline highlighting main points to be addressed when starting to succession plan.
Needs:
Determine your objectives- what do you want? For you, your family and your business. (Business’ financial needs)
What are your shares of the business worth? (Business value)
What are your personal financial needs- ongoing income needs, need for capital (ex. pay off debts, capital gains, equitable estate etc.)
There are 2 sets of events that can trigger a succession plan: controllable and uncontrollable.
Controllable events
Sale: Who do you sell the business to?
Family member
Manager/Employees
Outside Party
There are advantages and disadvantages for each- it’s important to examine all channels.
Retirement: When do you want to retire?
What are the financial and psychological needs of the business owner?
Is there enough? Is there a need for capital to provide for retirement income, redeem or freeze shares?
Does this fit into personal/retirement plan? Check tax, timing, corporate structures, finances and family dynamics. (if applicable)
Uncontrollable Events
Divorce: A disgruntled spouse can obtain a significant interest in the business.
What portion of business shares are held by the spouse?
Will the divorced spouse consider selling their shares?
What if the divorced spouse continues to hold interest in the business without understanding or contributing to the business?
If you have other partners/shareholders- would they consider working with your divorced spouse?
Illness/Disability: If you were disabled or critically ill, would your business survive?
Determine your ongoing income needs for you, your spouse and family. Is there enough? If there is a shortfall, is there an insurance or savings program in place to make up for the shortfall amount?
Will the ownership interest be retained, liquidated or sold?
How will the business be affected? Does the business need capital to continue operating or hire a consultant or executive? Will debts be recalled? Does the business have a savings or insurance program in place to address this?
Death: In the case of your premature death, what would happen to your business?
Determine your ongoing income needs for your dependents. Is there enough? If there is a shortfall, is there an insurance or savings program in place to make up for the shortfall amount?
Will the ownership interest be retained, liquidated or sold by your estate? Does your will address this? Is your will consistent with your wishes? What about taxes?
How will the business be affected? Does the business need capital to continue operating or hire a consultant or executive? Will debts be recalled? How will this affect your employees? Does the business have a savings or insurance program in place to address this?
Execution: It’s good to go through this with but you need to get a succession plan done. Besides having a succession plan, make sure you have an estate plan and buy-sell/shareholders’ agreement.
Because a succession plan is complex, we suggest that a business owner has a professional team to help. The team should include:
Financial Planner/Advisor (CFP)
Succession Planning Specialist
Insurance Specialist
Lawyer
Accountant/Tax Specialist
Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU)
Contact us about helping you get your succession planning in order so you can gain peace of mind that your business is taken care of.
Financial Planning for business owners is often two-sided: personal financial planning and planning for the business.
Business owners have access to a lot of financial tools that employees don’t have access to; this is a great advantage, however it can be overwhelming too. A financial plan can relieve this.
A financial plan looks at where you are today and where you want to go. It determines your short, medium and long term financial goals and how you can reach them. For you, personally and for your business.
Worry less about money and gain control.
Organize your finances.
Prioritize your goals.
Focus on the big picture.
Save money to reach your goals.
For a business owner, personal and business finances are connected. Therefore both sides should be addressed: Personal and Business.
There are 2 main sides your business financial plan should address: Growth and Preservation
Growth:
Cash Management- Managing Cash & Debt
Tax Planning- Finding tax efficiencies
Retaining & Attracting Key Talent
Preservation:
Investment- either back into the business or outside of the business
Insurance Planning/Risk Management
Succession/Exit Planning
There are 2 main sides your financial plan should address: Accumulation and Protection
Accumulation:
Cash Management – Savings and Debt
Tax Planning
Investments
Protection:
Insurance Planning
Health Insurance
Estate Planning
Establish and define the financial planner-client relationship.
Gather information about current financial situation and goals including lifestyle goals.
Analyze and evaluate current financial status.
Develop and present strategies and solutions to achieve goals.
Implement recommendations.
Monitor and review recommendations. Adjust if necessary.
Talk to us about helping you get your finances in order so you can achieve your lifestyle and financial goals.
Feel confident in knowing you have a plan to get to your goals.
Many business owners have built up earnings in their corporation and are looking for tax efficient ways to pull the earnings out to achieve their personal and business financial goals such as:
building and protecting your savings
providing for loved ones
planning for retirement
What’s the purpose of the investment? First, think about what you’ll be doing with your savings. This will help dictate what savings vehicle is best suited for your situation. Then consider the following factors:
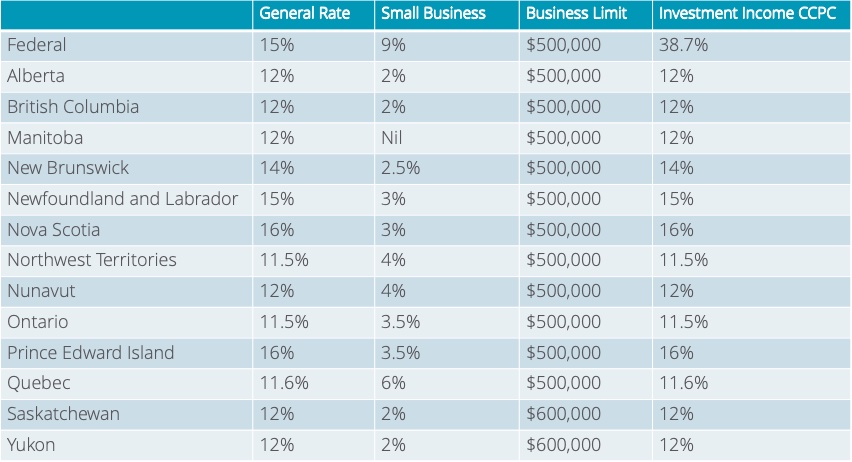
Taxes: As a small business owner, you have access to the small business tax rate which is typically lower than your personal tax rate. (See table below.) Also, as of January 1, 2019, the Federal Budget decreased the small business limit for corporations with a set threshold of income generated from passive investments.
2019 Corporate Income Tax Rates
Timing: You can control the timing of the payout which means you could potentially defer paying out the money until you need it and determine if you’d like to pay it out as salary or dividend.
Creditor Protection: Sometimes, investments held inside a corporation can be vulnerable to creditors, therefore you may want to consider using a holding company or trust or pay out money to yourself personally. This can be complex and requires professional advice.
Capital Gains Exemption: If your investment grows too large, it may endanger your qualification for the lifetime capital gains exemption that ‘s available when shares of a qualified small business corporation are sold or transferred.
For business owners, before investing personally or corporately, it’s certainly worth seeking professional advice to ensure that it suits your individual circumstances.
Business owners can be busy… they’re busy running a successful business, wearing lots of hats and making a ton of decisions. We’ve put together a list of 10 essential decisions for every business owner to consider.
10 essential decisions for a business owner from considering corporate structure to retirement and succession planning.
The essential questions include:
Best structure for your business (ex. Sole Proprietor, Corporation, Partnership)
Reduce taxes
What to do with surplus cash
Build employee loyalty
Reduce risk
Deal with the unexpected
Retire from your business
Sell your business
Keep your business in the family
What to do when you’re retired
As a financial advisor, we are uniquely positioned to help business owners, talk to us about your situation and we can provide the guidance you need.
Troy Andersen
Certified Financial Planner®
President
Tel: 604-341-5686
Email: troy@pafinancial.ca
16741 – 84A Avenue
Surrey, BC
V4N 4W2
We specialize in providing consulting for Employee benefits including group investment products and Executive benefits and make it understandable for our clients. Service is the cornerstone of our firm. We serve a broad array of clientele; from small businesses to large corporations. As every client is unique we take pride in understanding our clients’ needs and helping them achieve their goals. Being true independent brokers, we only work for our clients and not for any one insurance company. Service matched with solid processes and integrity are the cornerstones of our company. We look forward to working with you now and in the future.

